产品展示PRODUCTS SHOW
首页>产品展示>Main technologies

Adsorption and Regeneration of Activated Carbon
The activated carbon which is divided basically into two categories is widely used in many industries. They are powdered activated carbon (PAC) and granular activated carbon (GAC). Normally, the former has a particle size of less than 60 meshes and the latter has a particle size more than 40 meshes. Compared with powdered activated carbon, granular activated carbon may have a higher price and a larger investment. However, when the granular activated carbon is saturated, it can be regenerated by a regenerated furnace in order to regain the adsorption performance of the activated carbon, which can be cycled many times.Therefore, the granular activated carbon is not only high cost performance, but also friendly to the environment. Surprisingly, it can achieve a high degree of automation to use granular activated carbon (GAC) instead of powdered activated carbon (PAC).
1. Application
1.1 The activated carbon is widely used in the field of food, including the purification of gases and water, and the decolorization of sugar, Such as the liquid purification, decolorization, dechlorination and deodorization in beverage, wines and purified water. Adsorption and decolorization of sugar liquid (starch sugar, sucrose, etc.).
1.2 It is widely used in the field of environment management, such as water treatment–purified water purification, advanced treatment of sewage; flue cleaning–desulfurization and denitrification of flue gas, the treatment for volatileorganic matter and so on.
1.3 It tends to use in other fields such as chemical and metallurgy industries, etc.,including purification and solvent recovery.
2. Principle
2.1 Adsorption Principle
Granular activated carbon utilizes its large specific surface area and internal pore structure to adsorb various impurities. It is strong general adsorbent showing little specificity in the sense that one colorant is adsorbed to the exclusion of another. Inparticular, the activated carbon removes almost all the flavonoid colorants in the feed liquor and carbon is also effective in removing most phenolic compounds.
2.2 Adsorption Process of Activated Carbon
In the installations with activated carbon, liquor flow is down through the carbon bed held in the column, so impurities are adsorbed both on the surface of the carbon and in the pores of the carbon particles. The purpose of impurity removal is sufficiently achieved by controlling the time of the liquid to be removed stays in the carbon layer. Sugar colorants are so tightly adsorbed that thermal reactivation at 900 to 1000°C is almost universal.
2.3 Regeneration Principle
The carbon regeneration is to remove the adsorbate on the activated carbon pores by physical,chemical or biochemical methods on retaining the original structure of the activated carbon in order to regain its adsorption performance as well as cycle use.
2.4 Activated Carbon Regeneration Methods
There are many methods for activated carbon regeneration, such as thermal regeneration,biological regeneration, chemical solution regeneration, wet oxidation regeneration, super critical extraction regeneration, electrochemical regeneration, ultrasonic regeneration, and microwave irradiation regeneration. Various method each has its characteristic. At present, the activated carbon production and regeneration method widely used at home and abroad is a thermal regeneration method, especially widely used in the sugar production process because of its relatively high reaction efficiency. When the activated carbon is regenerated by the method, a variety of furnace types from which you can choose are the multi-hearth furnace, the horizontal rotary furnace, the fluidized bed furnace and the Stepple furnace. The multi-hearth furnace is the most widely used in many fields. Large production enterprises in our country gradually put the multi-hearth furnace to production lines aiming at improving the product quality and enlarging production scale. The structure diagram of the multi-hearth furnace is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1 Schematic diagram of multi-hearth furnace (6 layers)
Multi-hearth furnaces named after the furnace with many layers (or sections) are also called multi-stage furnaces. The number of furnace layers depends on the material to be processed.There are generally 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 15, 16 or 17 floors. For the large-scale production enterprises of activated carbon, 15, 16 or 17 layers are most widely used. The shell of the multi-hearth furnace is a steel cylinder body, and the inner liner is made of refractory material or heat insulating material. Each layer of horizontal circular hearth is installed at a certain distance along the vertical direction of the furnace. Every hearth has unloading holes. and the opening position from the top to the bottom is a hole in the center of the single layer, and several holes on the edge of the double layer. The center of the furnace body is a hollow shaft with jacket and rabbles are arranged aroundwith it. The rabbles are symmetric but different with those of other hearths.
According to the end use of products, each layer temperature of the multi-hearth furnace can be controlled to produce kinds of products with different qualities flexibly and elastically. We can control the retention time by adjusting the moving speed of the materials in the regeneration furnace. Thus, the goal that retention time is different during the different temperature ranges can be achieved accurately. At the same time,the retention time for materials in each hearth is different from each other hearth.
2.5 The Regeneration Process
The regeneration process of granular activated carbon involves the following steps:
- Dewatering, use the plants by gravity settling to separate the wet activated carbon from the water.
- Drying,dry the wet saturated activated carbon with a simple drying equipment.
- Volatilization/Distillation,distill or carbonize the adsorbate.
- Gasification, the remaining in the pores of activated carbon is reactivated or regenerated via re-oxidization.
Finally, activated carbon after regeneration is discharged into the quench tank for cooling and then sent back to the whole adsorption system through the blowing tank to wait for the newadsorption cycle.
3. Structure Introduction

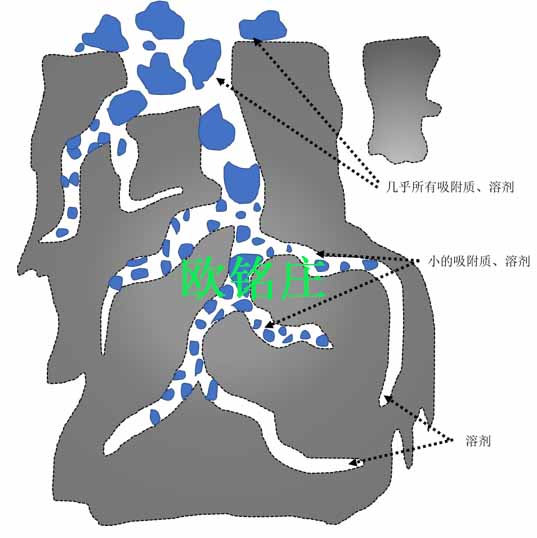
Figure 3Internal pore structure of granular activated carbon
4. Advantage
In the starch sugar industry, the most mature refining section often requires the cooperation of activated carbon and ion exchange resin to completely remove organic impurity molecules, protein sand inorganic salt ions. In the process, the activated carbon process should beplaced before the ion exchange process. Most of impurities, especially pigments, can be removed in time. Only in this way can the service life of ion exchange resin be greatly extended. Therefore, the activated carbon is very important for the refining process and plays a very important role especially in the decolorization of starch sugar.
The whole system of adsorption and regeneration of granular activated carbon generally includes: adsorption columns, activated carbon and water circulation system, regeneration furnace,waste-heat-recovery boiler and tail gas cleanup system, etc. There is lots of spent carbon produced during the production and application. It needs a large place to disposal. If it is not recycled and reused, environment would be polluted badly by it, also lots of resources would be wasted. Therefore, it is very necessary for large factories to have the regeneration of activated carbon, whatever we try to take it into account in environmental and economic issues as well.
The activated carbon thermal regeneration method is currently the most widely used and the most mature regeneration method in the industry. The regeneration method is to heat the spent carbon. And then the organic matter adsorbed by the activated carbon is carbonized and decomposed at a high temperature. Finally, the gas escapes, thereby the spent carbon turns to activated carbon. The high-temperature thermal regeneration method can remove the organic matters adsorbed on the activated carbon while removing the inorganic salt deposited on the surface of the carbon. At the same time, the new micro pores are generated in the carbon, and the activity of the carbon is fundamentally recovered.
The advantages of a multi-hearth furnace for thermal regeneration are as follows:
(1) The material in the furnace is slowly and continuously turned by the rabbles and the rake tooth driven by the central shaft. We can control the shaft rotation speed and adjust the angle of rake tooth by the middle shaft motor to have the reaction time what we need.
(2) Independent burners at corresponding layer of the furnace in order to accurately control temperature to meet the requirements of application of multi-hearth furnace inactivated carbon industry and at each activation stage.
(3) Accurate control of gas volume and activation process to keep feed and discharge continuous,and ensure products are of satisfactory quality.
(4) Under the continuous turning action of the rabbles and the rake tooth, the contactarea between the surface of the material and the gas is increased, and theactivation rate and the quality of the product are improved.
(5) Vertical structure is possessed of small land occupation and high processing capacity.
In summary, the thermal regeneration method has good general performances, high regeneration efficiency.It can complete the regeneration of granular carbon (30 min to 60 min) in ashort time. The method is not only basically non-selective to the adsorbate, and has no regeneration waste to produce. However, there is generally 5-10% carbon loss in the process of thermal regeneration. The mechanical strength of recycled activated carbon is slightly decreased, and heat sources are needed in the process of thermal regeneration. The short-term investment cost is expensive,but in the long term, single-time average operation is greatly reduced. After the thermal regeneration of activated carbon, the adsorption efficiency will be reduced a little. Thus, most of the adsorption performance will be lost after several cycles.
However, considering the combination of granular activated carbon adsorption system and regeneration system, and balancing investment and operating costs, it is no doubt that the granular activated carbon column and regeneration furnace are the best choice for long-term production.
5. Engineering cases
5.1 Our company has successfully cooperated with domestic famous starch company.
in which the adsorption decolorization system and regeneration system in the sugar workshop have been put into production. Stable running and good effects are all the time.
This project uses the thermal regeneration activation method to regenerate the activated carbon. The furnace is a multi-hearth furnace, and the entire regeneration process can be completed in the furnace. The method has the advantages of good regeneration effect and high efficiency. The adsorption and regeneration process of granular activated carbon is shown in Figure 4.
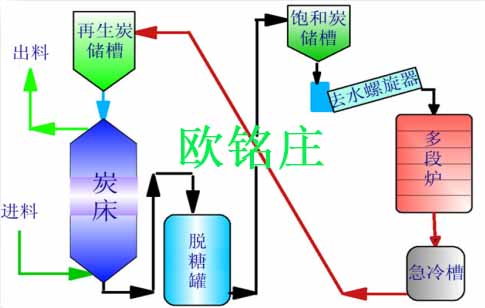
Figure 4 Adsorption and regeneration process of granular activated carbon
The reason why it can complete the regeneration process of granular activated carbon in the regeneration furnace is mainly the regeneration effect can be ensured by controlling the chemical reaction occurring during regeneration. The main purpose of regeneration is to remove the impurities absorbing in the granular activated carbon, and then put spent carbon back to where it was before. (generally, the granular activated carbon has several numbers of regenerations about 5 to 6 times due to its limited mechanical properties). The adsorption system sends the saturated activated carbon to a carbon storage tank, which is the beginning of the regeneration system. The wet saturated activated carbon contains different organic impurities, and a large part of the adsorbate and water contained in the saturated activated carbon are existed in the micropores of the activated carbon particles. The first step of regeneration uses a gravity-dewatering dewatering mechanism to separate the wet activated carbon from the water. The second step uses a simple drying to dry the wet saturated carbon.In the third step, the adsorbate is distilled or carbonized. The fourth step is we can make the remaining carbides oxidative well, which is what we called reactivation or regeneration.
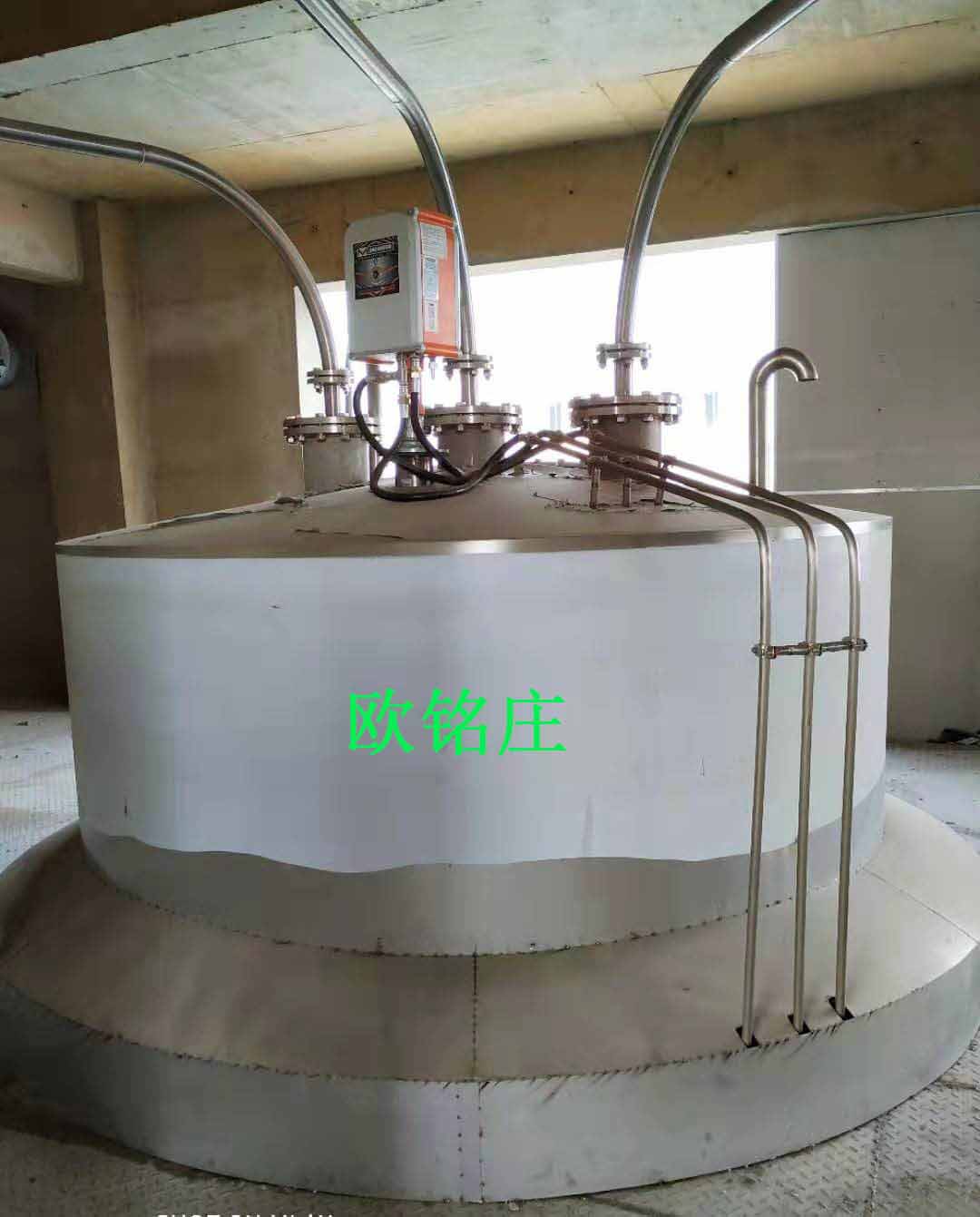

Figure 5 The site map of storage carbon tank of regeneration
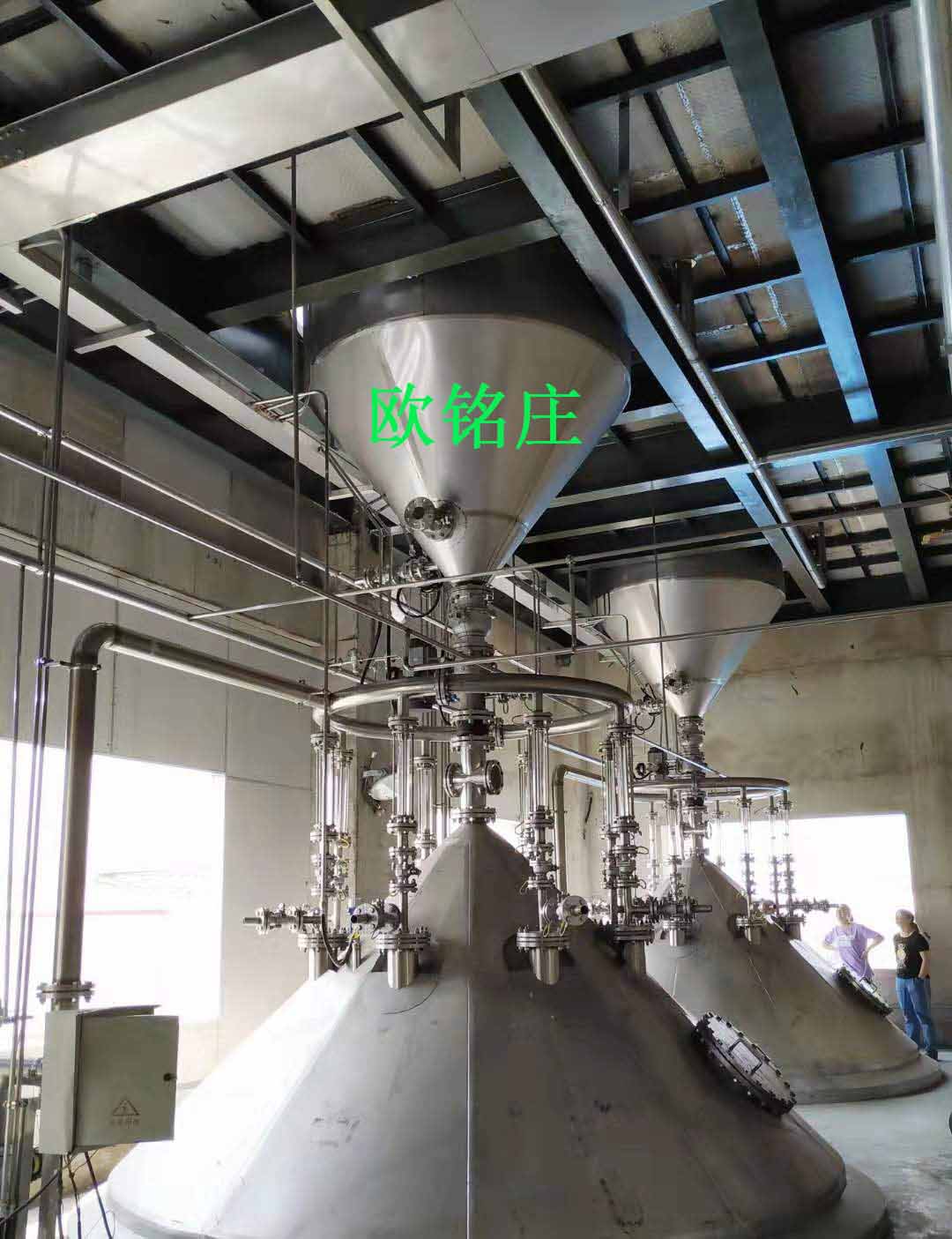



Figure 8 The sketch of granular activated carbon column groups for sucrose decolorization
Our company has fully followed up all the projects, constantly optimized the details, and improved. In any case, we have always been committed to providing quality services to our customers.
【上一个】 Chromatographic separation system
【下一个】 Liquefaction system






